Do you eat a healthy diet, then wonder why you are bloated and gassy? It could be due to poor food layering habits! Proper food combining has not been something we were traditionally taught, especially in American culture, where cheeseburgers, apple pies and casseroles are the norm.
Let’s take it back 5,000 years and look at the historical research that suggests these go-to classics could be the culprit to your indigestion and poor gut health. Many cultures and religions over the years have defined how you should eat, but the majority of these practices have not found their way to our dinner tables.
According to Ayurveda “food layering” is the concept of eating compatible foods together to support digestion and gut health. It is based on the idea that different foods have distinct digestive properties, and combining certain foods can either aid or hinder digestion. Through understanding food layering, we can make choices that enhance our body's ability to process nutrients and maintain a harmonious internal environment.
 Principles of Food Layering
Principles of Food Layering
When incompatible foods are consumed together, the digestive tract can become inefficient, leading to problems such as bloating, gas, and indigestion. Your body requires different enzymes and acid levels to break down each type of food.
Here are some of the basic rules to follow:
• Eat fruits alone as fruits digest quickly and can easily ferment in the gut. Fruits get stored as fat instead of burned as energy when combined with other foods. Melons specifically cannot be mixed with other fruits or foods. Bananas can turn toxic when mixed with dairy products.
• Avoid mixing different proteins together, such as meat and cheese. Dairy, meat, eggs and tofu should not be combined together or combined with starches, such as beans.
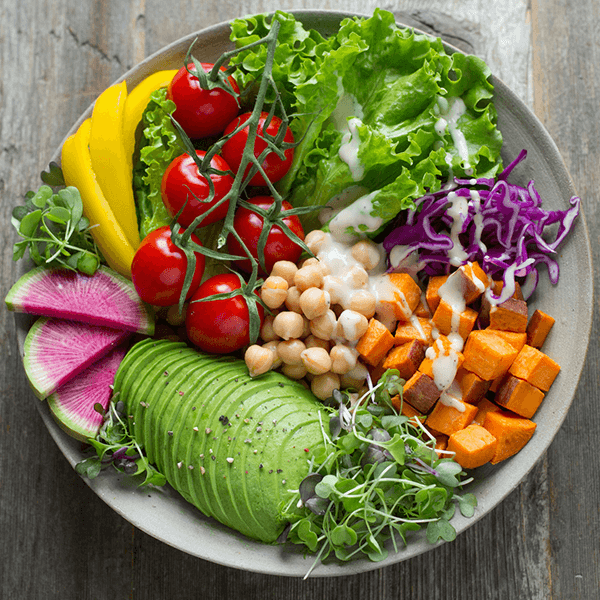
• Vegetables do not go well with fruit or milk and should be combined with grains, beans, dairy or meat.
• Cheese should not be eaten with fruit, beans, other dairy products or hot drinks. Use with grains and vegetables instead.
• Yogurt should not be mixed with fruit, beans, fish, other dairy, nightshades or hot drinks.
• Avoid eating eggs with milk, cheese, yogurt, fruit, potatoes, beans or meat.
You can find helpful charts online that go into specific detail on best practices.
 Benefits of Food Layering
Benefits of Food Layering
Following new practices and changing up your favorite recipes can seem like a daunting task, but there are many benefits to doing so! Here are just a few of the benefits you may experience:
• Proper food layering can reduce bloating, gas, and indigestion.
• Compatible food combinations support efficient nutrient absorption.
• Avoiding incompatible foods can prevent energy crashes and help you maintain steady energy levels.
• Balanced digestive practices support overall health and can reduce the risk of chronic conditions.

Enjoy A Healthy, Happy Gut
Over time, chronic poor food layering can have more severe consequences for gut health and overall well-being, like autoimmune diseases, allergies, and even mental health disorders. So it is imperative to understand and practice proper food layering and combining to maintain a healthy & happy gut and prevent long-term health complications.
- - - - - -
Kellie is a Certified Ayurvedic Digestive Health Coach, Yoga Teacher, and an inspired foodie! After battling autoimmune issues, she found wellness through a gluten-free and vegetarian lifestyle. Her goal is to promote healthy living and inspire others to feel good. Thank you Kellie for such a wonderful article!